Contents
Haemophilus influenzae Disease Surveillance and Trends
要点
- CDC 使用 2 个监测系统追踪侵袭性流感嗜血杆菌病。
- 侵袭性疾病是指细菌侵入通常没有细菌的身体部位,如血液。
- CDC 不追踪非侵入性流感嗜血杆菌疾病,例如耳部感染。

数据系统
国家法定报告疾病监测系统
侵袭性流感嗜血杆菌病是一种国家法定报告疾病。
CDC 通过国家法定报告疾病监测系统 (NNDSS) 收集有关侵袭性流感嗜血杆菌病的全国信息。CDC 每周都会收到 NNDSS 数据。
继续阅读:了解有关 NNDSS 的更多信息
Active Bacterial Core 监测
CDC 还通过活性细菌核心监测 (ABC) 从该国 10 个地区的实验室收集信息。ABC 是 CDC 新发感染计划的一部分。
继续阅读:活性细菌核心监测 (ABC)
Bact 事实互动
您可以分析和可视化 ABC 流感嗜血杆菌数据。
如何解释数据
疾病趋势
自美国开始使用 Hib 疫苗以来,侵袭性流感嗜血杆菌病的流行病学发生了变化。儿童 Hib 疫苗接种于 1987 年开始,婴儿接种于 1990 年开始。
从那时起,5 岁以下儿童侵袭性疾病的年发病率发生了变化:
- b 型:减少 99%
- 非 b: 递增(主要是类型 a 和 f)
- 非定型:增加
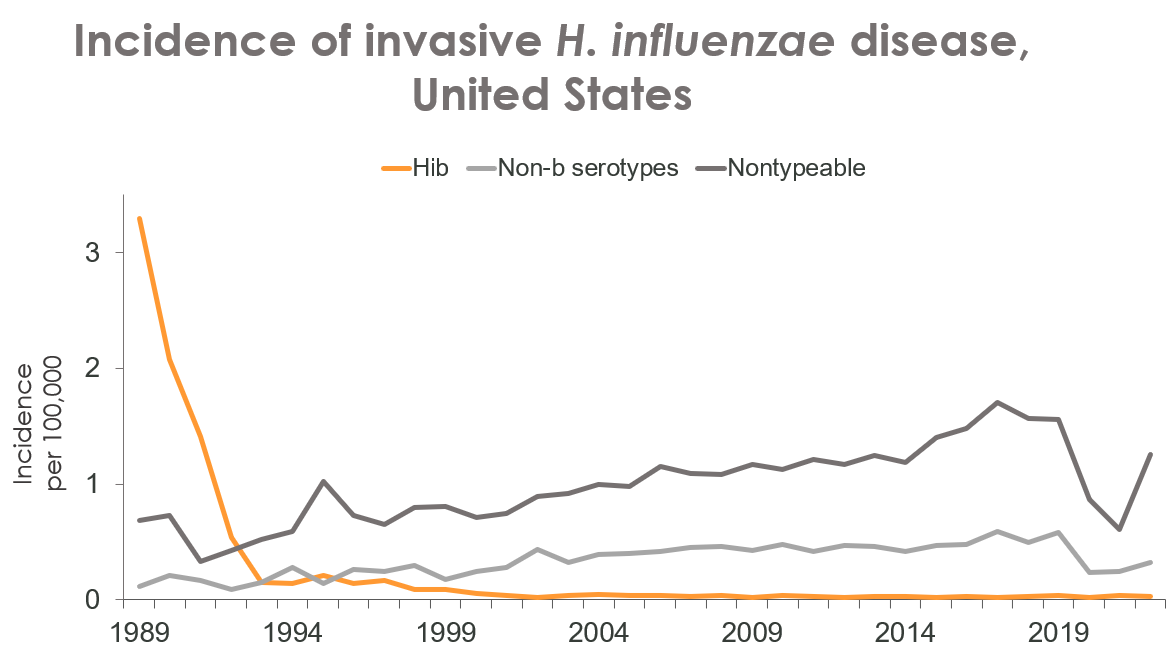
来源:Active Bacterial Core 监测
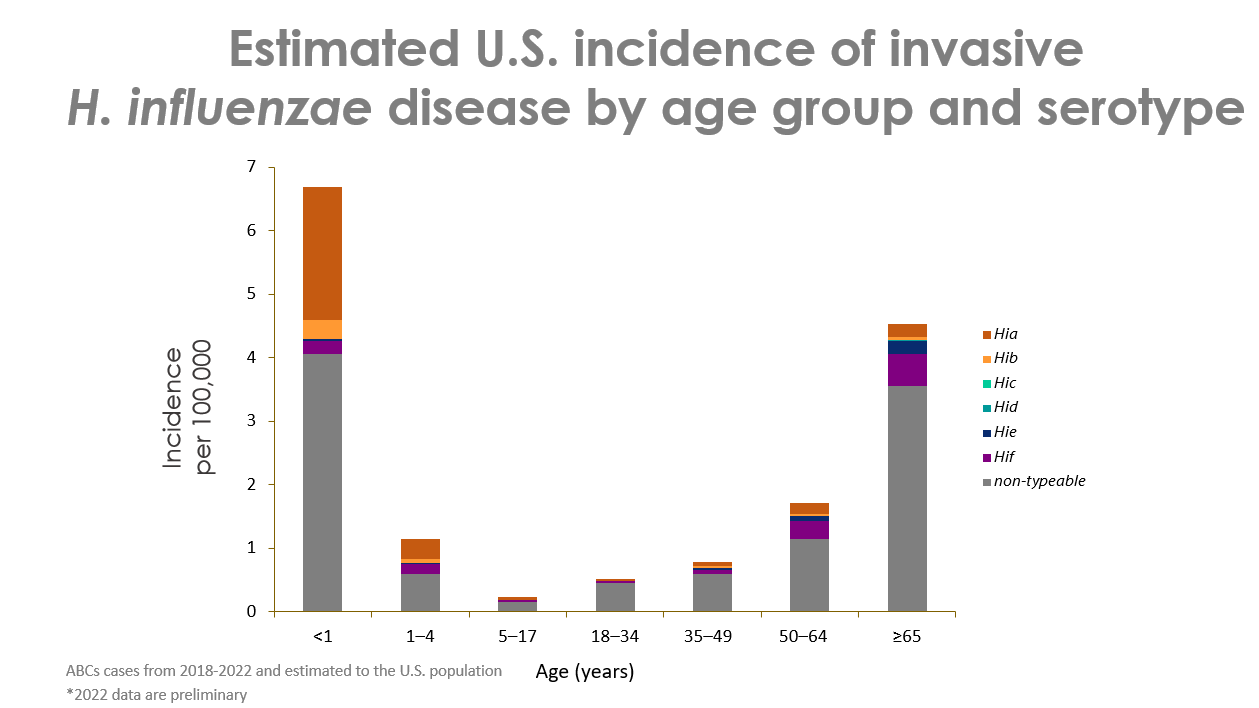
来源:Active Bacterial Core 监测
Hits: 52
